Are you a plant enthusiast looking to expand your collection? Plant propagations are a fantastic way to multiply your green babies and add new life to your indoor jungle or outdoor garden. However, knowing when or how to plant propagations is crucial for their successful growth. In this blog post, we will dive into the basics of plant propagation, equipping you with the knowledge to nurture these tiny plant cuttings into thriving specimens.

When to Propagate a Plant
-
Understand Your Plant's Growth Cycle: Each plant species has its own unique growth cycle, and understanding this cycle is key to knowing when to plant propagations. Typically, the best time to propagate is during the plant's active growth phase. This phase varies depending on the species, but it usually aligns with the spring and summer months when plants naturally experience a burst of growth.
-
Consider Seasonal Factors: Apart from the plant's growth cycle, there are a few seasonal factors to keep in mind when deciding when to plant your propagations. The first consideration is temperature. Most plants prefer warm temperatures for optimal root development, so it's best to avoid planting propagations during extreme cold or hot weather. Aim for a moderate temperature range where your plants can comfortably establish roots.
-
Observe the Parent Plant: The health and vigor of the parent plant can provide valuable cues for propagation timing. Wait until the parent plant is thriving and exhibiting robust growth before taking cuttings. A healthy parent plant ensures that the propagations receive ample nutrients and are more likely to thrive.
-
Timing is Everything: Once you've considered the growth cycle, seasonal factors, and observed the parent plant, it's time to determine the perfect moment for planting your propagations. I personally like to wait until there are a few inches of visible roots. Look for signs of growth and maturity in the cuttings themselves. Are there visible nodes or new leaves? These are indications that the cuttings are ready to be planted. Additionally, ensure that the cuttings have calloused over (formed a protective layer) before planting, as this helps prevent rot.
Plant Propagation Methods
When it comes to plant propagation, selecting the right growing medium is crucial for the successful development of roots and overall growth of the propagated plants. Here are some common types of growing mediums used in various propagation methods:
-
Potting Mix: Potting mix is a versatile growing medium widely used for propagating plants. It typically consists of a blend of organic matter such as peat moss, coconut coir, or compost, mixed with inorganic components like perlite or vermiculite to improve drainage. Potting mix provides a balanced combination of water retention and aeration, promoting healthy root development.
-
Seed Starting Mix: Seed starting mix is specifically designed for germinating seeds but can also be used for certain types of propagations. It is typically lighter and finer in texture than regular potting mix, allowing for optimal seedling development. Seed starting mix is often composed of peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite, providing excellent moisture retention and aeration.
-
Vermiculite: Vermiculite is a mineral-based growing medium known for its excellent water retention properties. It is often used for propagating seeds or cuttings that require high moisture levels. Vermiculite is lightweight and provides good insulation for root development. However, it lacks adequate drainage, so it is commonly mixed with other mediums for better aeration.
-
Perlite: Perlite is a volcanic glass that undergoes a heating process to expand into lightweight, porous granules. It is widely used as an additive in growing mediums for propagation. Perlite enhances drainage, prevents soil compaction, and promotes airflow around the roots. It is often combined with other mediums to improve aeration and prevent waterlogging.
-
Sand: Sand is a simple and inexpensive growing medium that provides good drainage for propagating certain plant species. It is commonly used for cuttings that are prone to rotting in overly moist conditions. However, pure sand is generally not ideal for all types of plants since it lacks nutrient content. It is often mixed with other mediums to improve its water-holding capacity.
-
Water: Water propagation is a method where plant cuttings are placed directly in water to encourage root development. Although not technically a growing medium, water serves as a medium for root growth in this method. It is important to change the water regularly to prevent stagnation and the development of harmful bacteria.
-
Soilless Mixes: Soilless mixes are growing mediums that are devoid of traditional soil. These mixes often combine various components like peat moss, coconut coir, perlite, vermiculite, and compost to create a well-balanced medium with optimal water retention and aeration. Soilless mixes are commonly used for seed germination, plug production, and hydroponic systems.
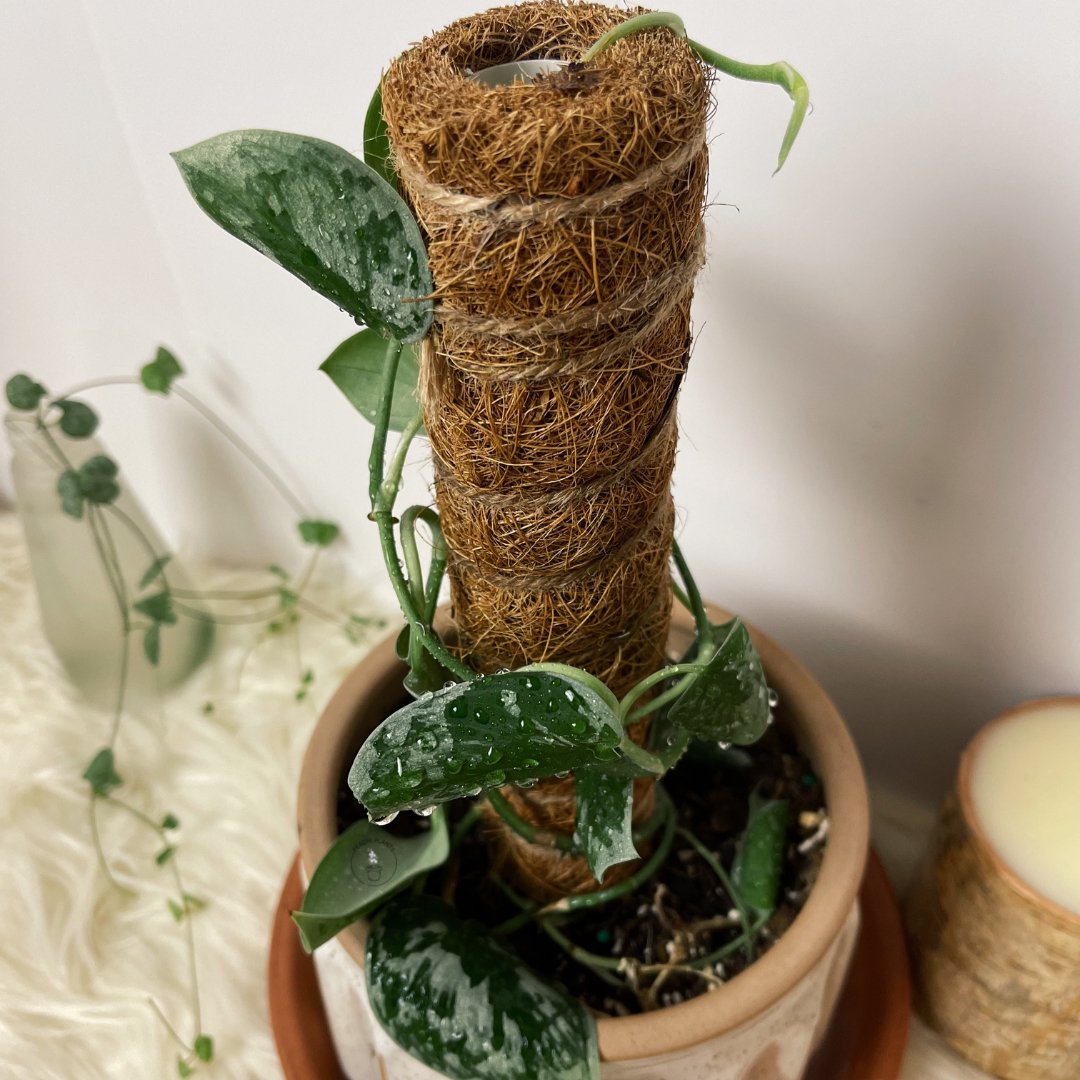
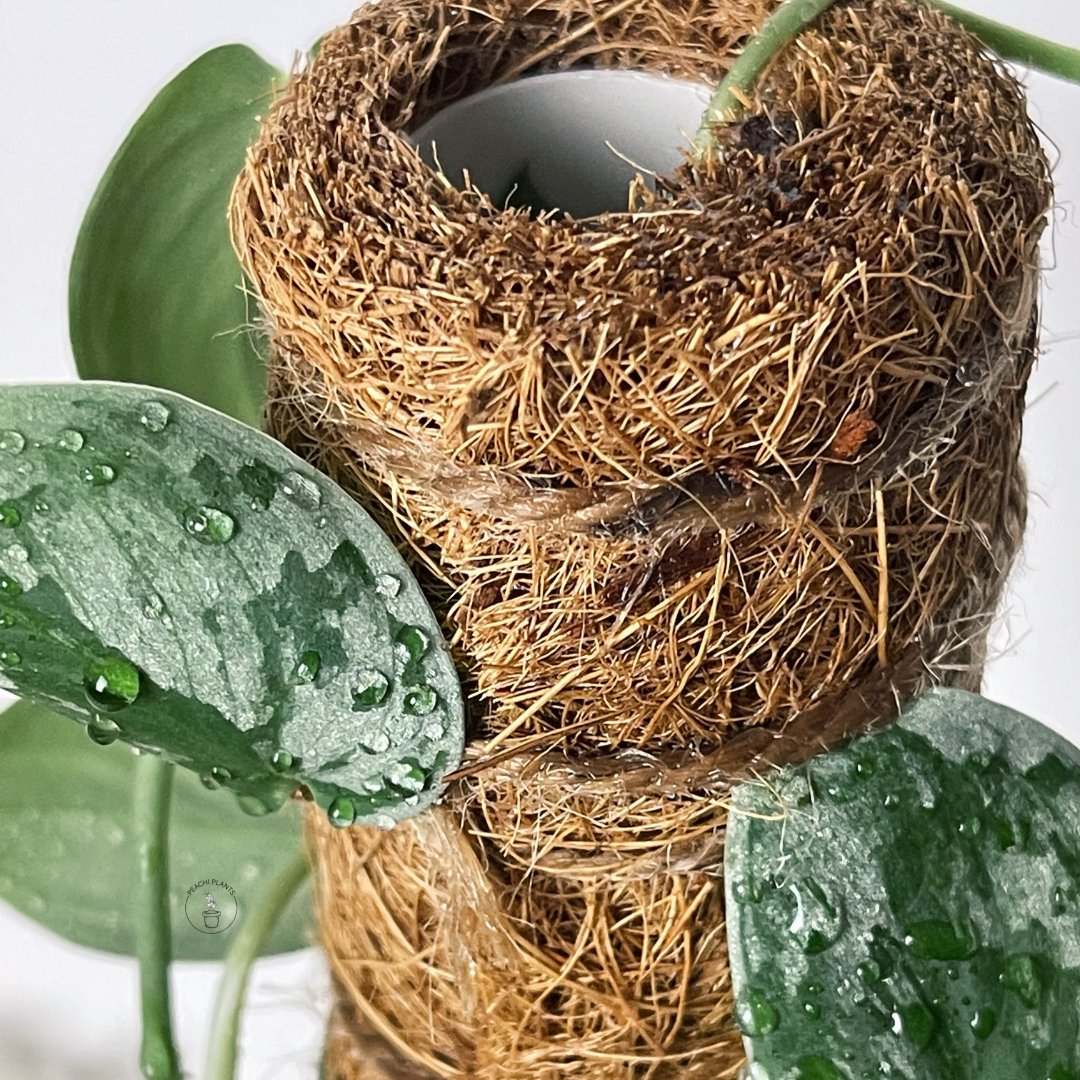
- Sphagnum Moss: Moss is a fantastic medium for propagating plants due to its unique properties. When used for propagation, sphagnum moss provides a moist and breathable environment that encourages root development. Its excellent water retention capabilities help keep cuttings consistently hydrated, reducing the risk of drying out. Additionally, sphagnum moss creates a protective barrier around delicate cuttings, shielding them from harsh environmental conditions.
It's essential to consider the specific needs of the plant species you're propagating when choosing a growing medium. Each medium has its advantages and is suitable for different propagation methods. Experimentation and experience will help you determine the ideal growing medium for the plants you wish to propagate, ensuring healthy and successful growth.
Common Houseplants You can Propagate
Plant propagation opens up a world of possibilities for expanding your plant collection and sharing the beauty of your favorite species. Many common houseplants can be successfully propagated, allowing you to create new plants from existing ones. Here are a few popular houseplants that are known for their ability to be propagated:
-
Pothos: Pothos is a versatile vining plant that can be propagated through stem cuttings in water or soil.
-
Spider Plant: Spider plants produce offshoots, commonly known as "spiderettes," which can be separated and planted individually to propagate new plants.
-
Snake Plant: Snake plants can be propagated through leaf cuttings or by dividing the root ball into smaller sections and repotting them.
-
Philodendron: Philodendrons are easy to propagate through leaf cuttings, which can be rooted in water or directly in the soil.
-
ZZ Plant: ZZ plants can be propagated by dividing the rhizomes or by taking leaflet cuttings and allowing them to root.
-
Peperomia: Peperomia plants such as pilea peperomioides can be propagated through leaf cuttings or by dividing up the root ball and repotting as a new plant.
-
Jade Plant: Jade plants can be propagated from stem cuttings, which should be allowed to callus before planting them in well-draining soil.
-
Rubber Plant/Ficus Elastica: Rubber plants can be propagated through stem cuttings, using either water or soil for rooting.
-
Aloe Vera: Aloe vera can be propagated by removing offsets or "pups" that grow around the base of the main plant.
-
Monstera: Monstera can be propagated through stem cuttings with a node and aerial root. Keyword aerial root, I have tried regular cuttings and it does not work. You must have an aerial root.
Remember, these are just a few examples of houseplants that can be successfully propagated. Each plant species may have specific requirements and methods, so it's essential to research and understand the particular propagation techniques that work best for the plants you wish to propagate.
How to Propagate a Plant:
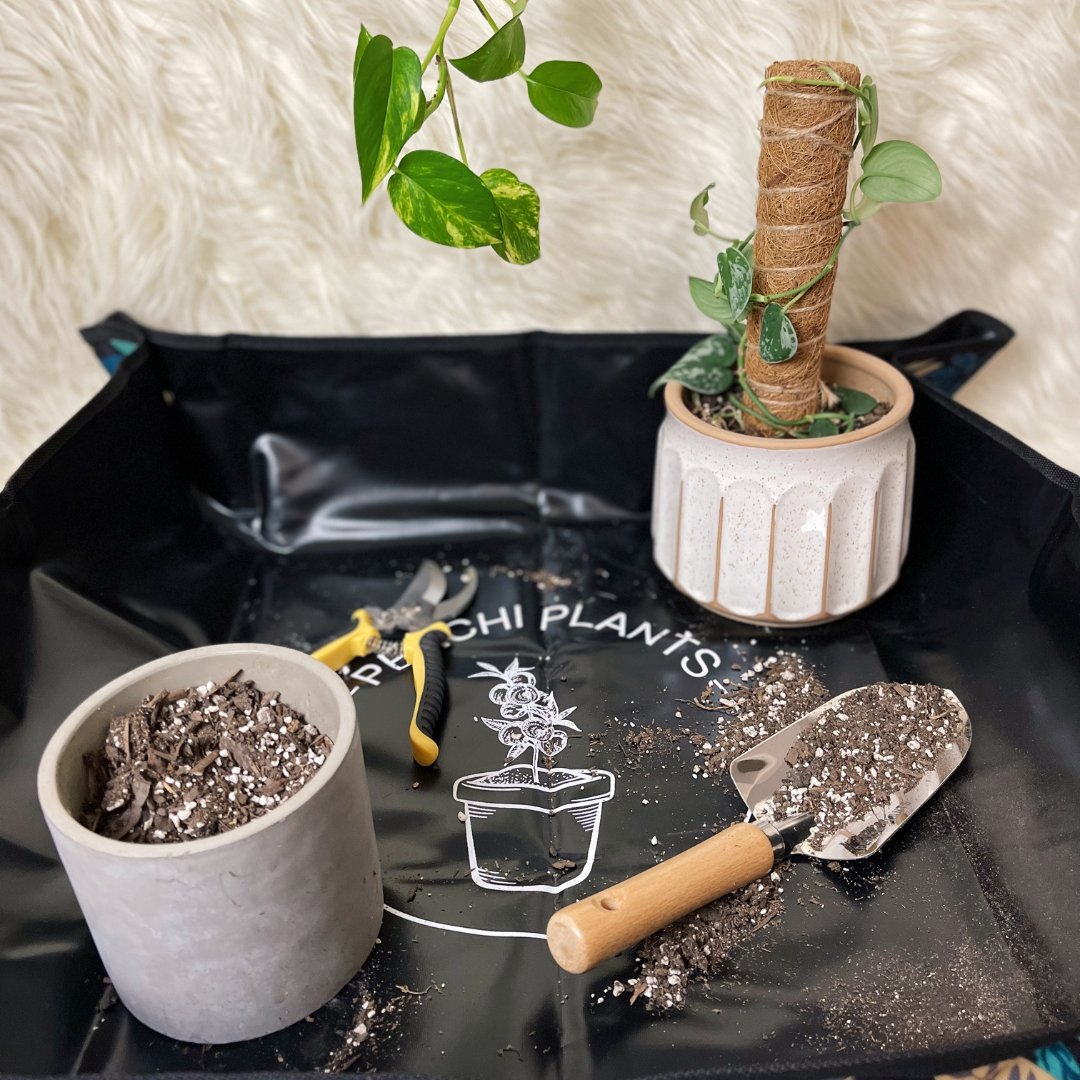
Taking a cutting is the first step towards propagating a new plant, and it's an exciting process that allows you to create duplicates of your favorite plants. Here's the steps on how to take a cutting for propagation:
-
Gather the Necessary Tools: Prepare a clean pair of pruning shears. Make sure to sterilize the tools with rubbing alcohol to minimize the risk of transmitting diseases.
-
Identify the Node: Examine the stem of the parent plant and locate a node. Nodes are the areas where leaves, branches, or buds emerge from the stem. They play a crucial role in root development.
-
Make a Clean Cut: Position the pruning shears just below the node. Make a clean, angled cut just above the node. Aim for a cutting that is approximately 4-6 inches long, depending on the plant species.
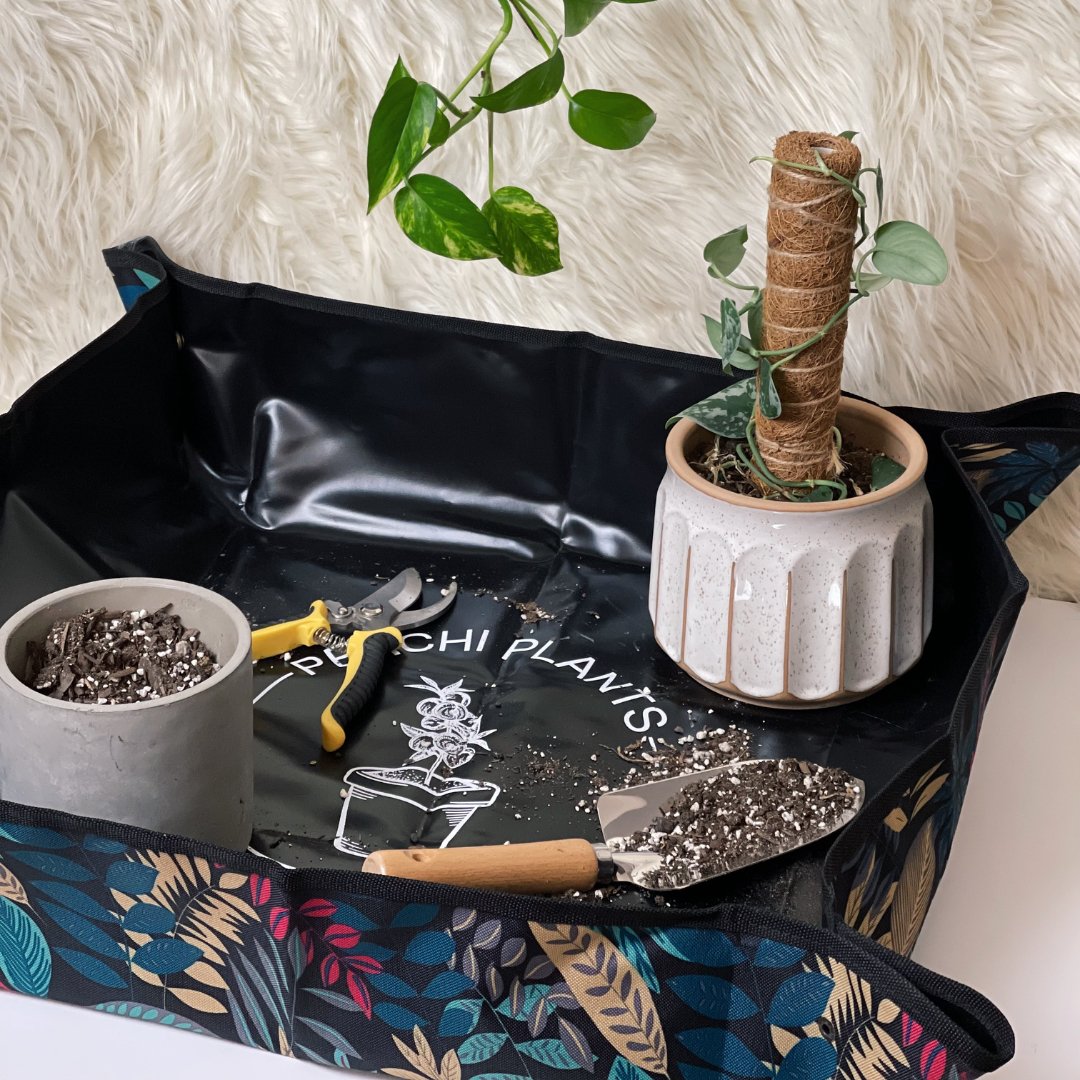
Transferring Your Propagation To Soil:
Potting up a propagation is an essential step in the journey of nurturing new plant life. Once your cuttings have developed roots and are ready for their own space, it's time to transfer them into individual pots. Here's the steps on how to pot up your propagations:
-
Select the Right Pot: Choose a pot that is appropriate for the size of your cutting and allows for some room for growth. Opt for a clean pot with drainage holes to prevent waterlogging.
-
Prepare the Potting Mix: Use a well-draining potting mix suitable for the specific plant you're propagating. A mix of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite is often a good choice. Fill the pot about two-thirds full with the potting mix.
-
Make a Hole: Create a small hole in the center of the potting mix using your finger or a dibber. The hole should be deep enough to accommodate the roots of the cutting.
-
Insert the Cutting: Gently place the cutting into the hole, ensuring that the roots are well-positioned and spread out. Hold the cutting upright as you backfill the hole with additional potting mix, gently pressing it down to secure the cutting.
-
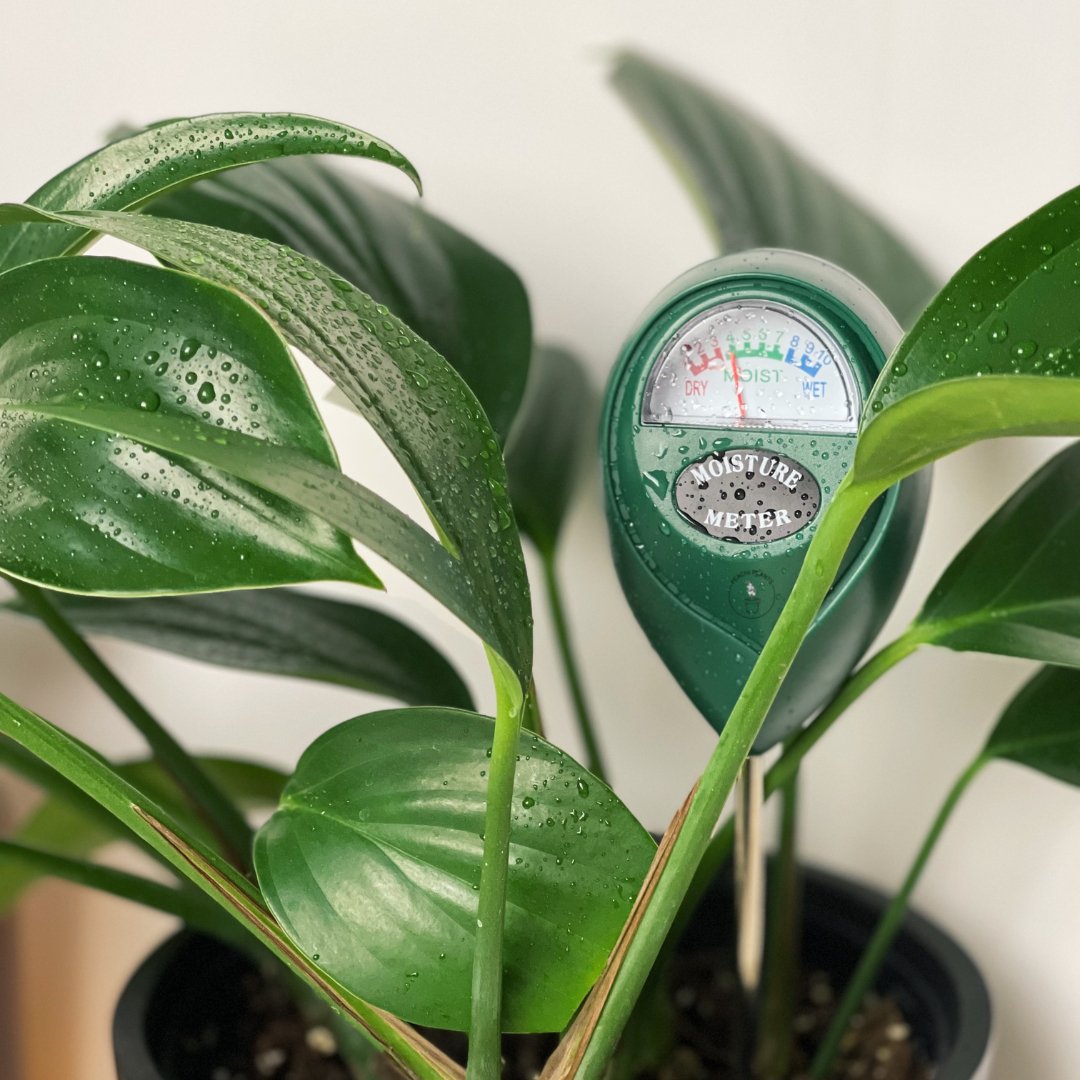
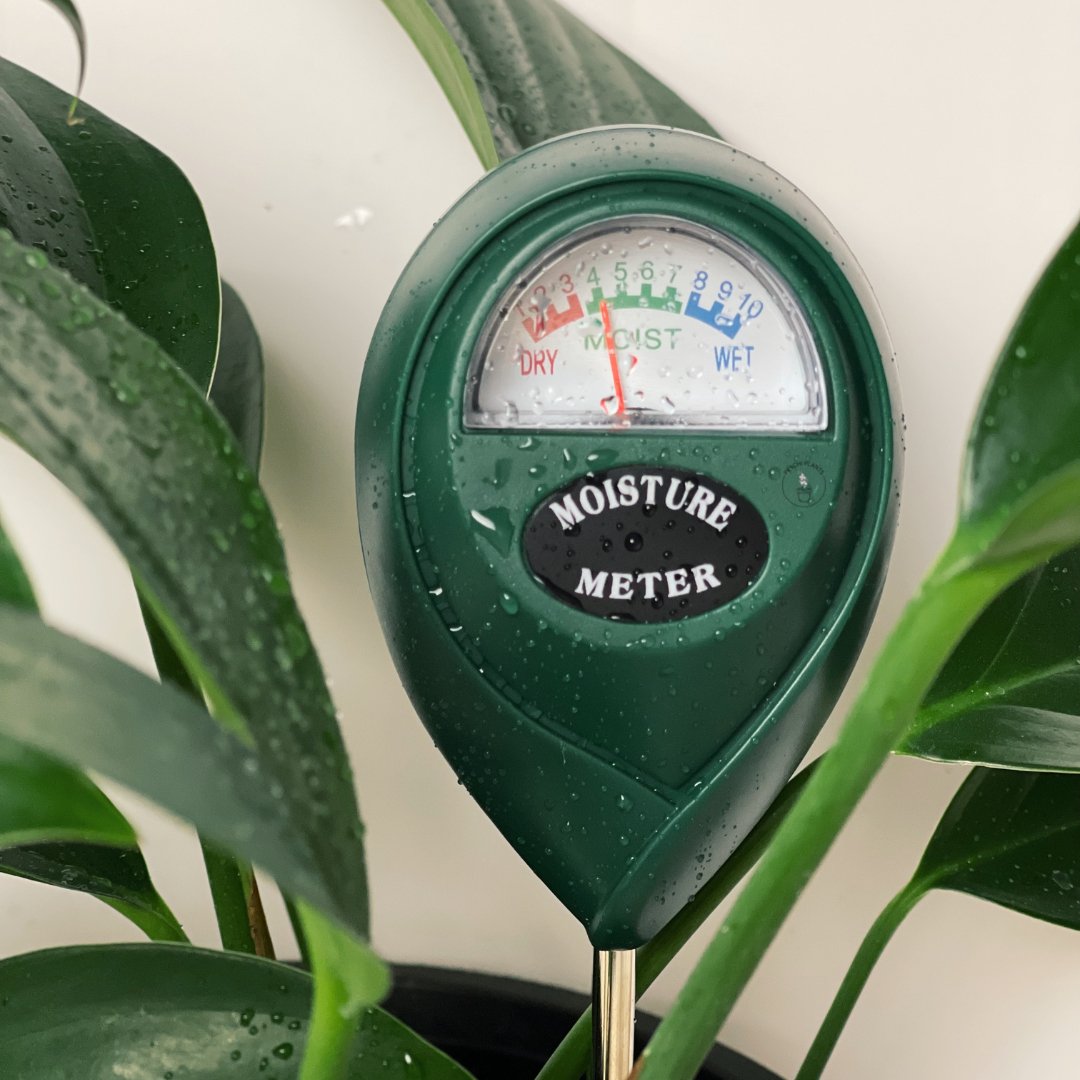
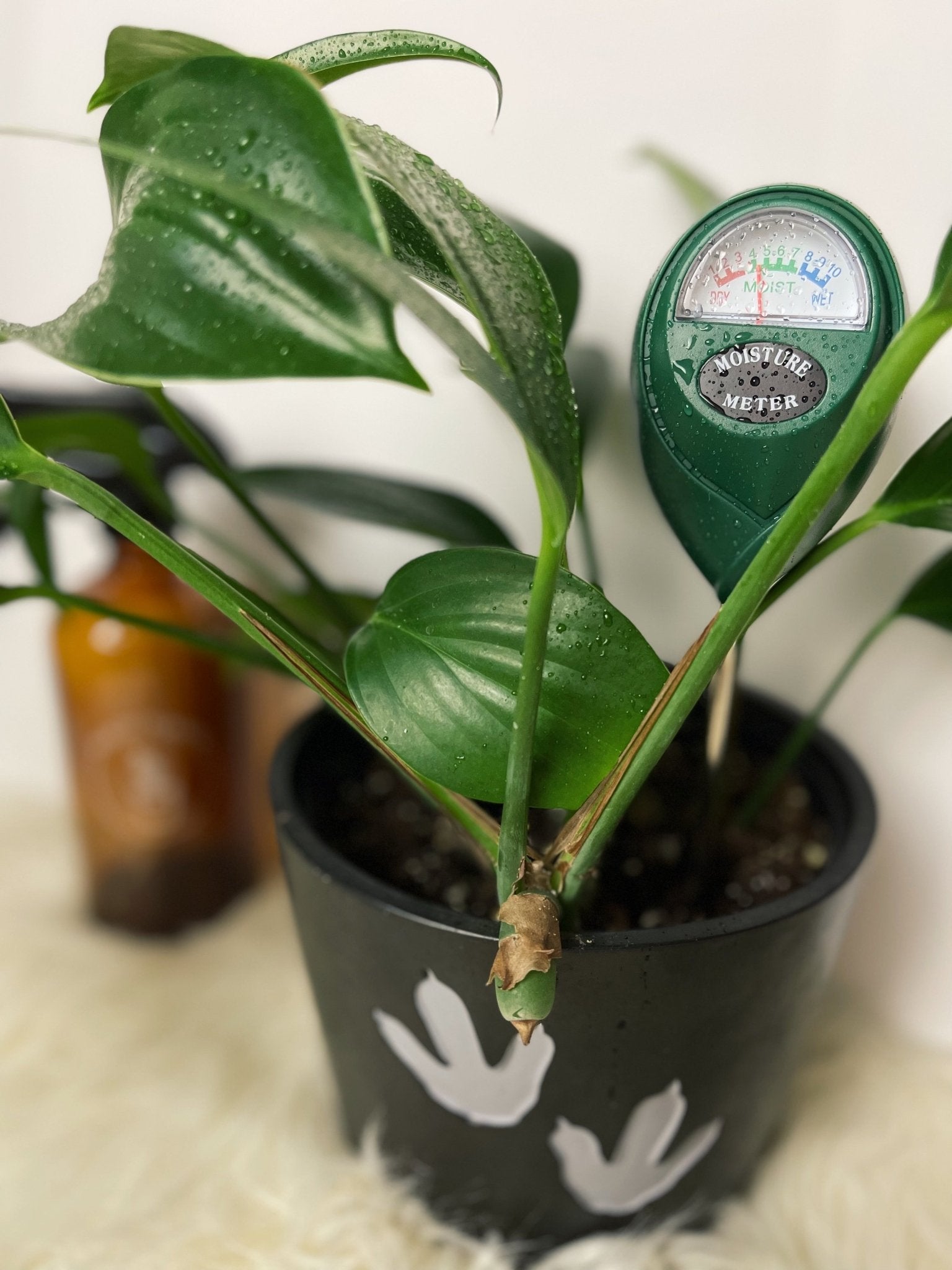
Water the Cutting: Give your newly potted propagation a thorough watering to settle the soil and provide moisture to the roots. Be careful not to overwater, as excess moisture can lead to root rot. A moisture meter is great way to prevent overwatering.
-
Provide Optimal Conditions: Place the potted cutting in a suitable location based on the plant's light and temperature requirements. Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy, and provide bright indirect light until the plant establishes itself.
-
Monitor and Adjust: Regularly monitor the moisture levels of the potting mix and adjust watering accordingly. Observe the growth and health of the propagated plant, making any necessary adjustments to its care routine.